Substance abuse and other psychiatric diagnoses are significant conditions that require an appropriate approach to diagnosis and treatment. In the United States of America, the DSM 5 diagnosis is essential for various important reasons. This article explains more about the DSM 5, including the necessary criteria, categories, and critics.
What is the DSM 5?
The DSM is an abbreviation representing the “Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.” However, “5” signifies “Fifth Edition.” DSM 5 is a 2013 update to the handbook by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). It contains all the significant mental health disorders for both children and adults.
The DSM 5 also includes details about the gender most affected by the mental illness.
Similar to medical conditions, both national institutes and insurance firms request a diagnosis to approve payment to treat mental health illnesses. Hence, mental health professionals use the DSM-5 to diagnose clients, treat them, and classify them appropriately for billing.
Significance and Changes in the DSM 5
The DSM 5 is the premier “living document” version of the typical DSM, where changes can be made. Note that the DSM-5 is similar to the DSM-IV-TR, but there are some significant differences between them.

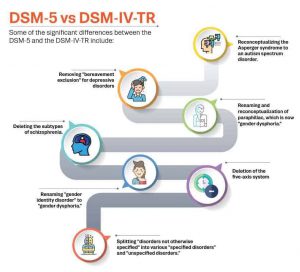
Some of the significant differences between the DSM-5 and the DSM-IV-TR include:
- Reconceptualizing the Asperger syndrome to an autism spectrum disorder.
- Removing “bereavement exclusion” for depressive disorders.
- Deleting the subtypes of schizophrenia.
- Renaming “gender identity disorder” to “gender dysphoria.”
- Renaming and reconceptualization of paraphilias, which is now “gender dysphoria.”
- Splitting “disorders not otherwise specified” into various “specified disorders” and “unspecified disorders.”
- Deletion of the five-axis system
Categories in the DSM-5
The ‘Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition’ most notably eliminated the conventional multi-axial system. Instead of that technique, it categorizes disorders with some related mental health conditions.
Here are some of the examples of the categories in the DSM-5:
- Anxiety disorders: Anxiety disorders describe the medical conditions relating to how the brain reacts to stress and potential danger. Note that these disorders are the most prominent in Europe. In a year, 14% of individuals aged 14 to 45 have the condition.
- Bipolar and related disorders: Bipolar disorders include mental health conditions that cause severe mood swings, including mania, hypomania, or depression.
- Depressive disorders: Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is a significant mood disorder characterized by features like a depressive mood, change in sleep patterns, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and more.

- Personality disorders: This category describes a group of mental illnesses that involve long-term patterns of behaviors or thoughts that are not healthy. Note that these issues also cause challenges with relationships.
- Eating disorders: There are over six common types of eating disorders. Examples include anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge eating disorder, pica, and rumination disorder.
- Obsessive-compulsive and related disorders: Commonly called OCD, the Obsessive-compulsive disorder is a mental condition that makes an individual have a specific thought repeatedly, which is also called obsession.
Compulsion describes the need to perform an activity. Both obsession and compulsion cause discomfort or impairment in the overall body functioning.
Substance Use Disorders: According to the DSM 5
The DSM 5 acknowledges addiction as meeting a number of criteria resulting from the use/misuse of any of these 10 drug classes:
- Alcohol
- Opioids
- Cannabis
- Hallucinogens
- Inhalants
- Sedatives
- Hypnotics
- Caffeine
- Stimulants
- Tobacco
Criteria for Substance Use Disorder
There are 2 substance-related categories in the DSM.
- “Substance-use disorders are patterns of symptoms resulting from the use of a substance that you continue to take, despite experiencing problems as a result.”
- “Substance-induced disorders, including intoxication, withdrawal, and other substance/medication-induced mental disorders, are detailed alongside substance use disorders.”
The DSM 5’s diagnostic criteria for Substance Use Disorder describe the essential requirements before concluding diagnosis. Here’s what you need to know for the eleven different standards:

- Tolerance: An individual’s body is more tolerant of substance use, requiring more help for the same drug effects.
- A high amount of time using: The individual typically takes their time using the substance for a specific effect.
- Withdrawal: When the individual stops using, they experience withdrawal symptoms. Withdrawal symptoms include changes in appetite, changes in mood, congestion, and more.
- Psychological or physical issues connected to use: Substance use causes certain physical medical conditions like lung cancer or liver damage. It may also result in psychological disorders like depression or anxiety.
- Failed attempts to control the use or stop: Individuals have made several attempts to cut back on substance abuse or quit, but it was unsuccessful.
- Neglected responsibilities due to use: This criterion describes individuals that may have failed in meeting specific duties at school, home, or work due to substance use.
- Hazardous use: Hazardous use defines persons that may have experiences of using the substance in ways that affect themselves and other individuals.
- Usage of more amounts or more extended use: In the DSM-5, this criterium defines individuals who started using more amounts of the substances. It also applies to individuals using them for more extended periods.
- Social challenges related to using: Substance abuse may result in significant relationship problems with a partner, family, or friends.
- Constant craving: This signifies that an individual may have experienced cravings for the substance, which is conventionally consistent.
- Quitting certain activities due to use: An individual may have skipped or stopped several activities due to substance abuse.
Critics of the DSM-5
Some relevant authorities have criticized the DSM-5 before and after its publication. According to some critics, many of the DSM-5 revisions or additions don’t have empirical support. Additionally, most disorders have low inter-rater reliability.
There are sections of the DSM-5 that also contain confusing or contradictory information. Some critics also claim that the psychiatric drug industry may have wrongly influenced the manual’s content. Note that the critics don’t change the importance of the handbook.
Updates and Revisions
Starting with the fifth edition of the DSM, there will be an incremental inclusion of the diagnostic guideline revisions. As changes in the DSM-5 occur, the updated versions will be recognizable via decimals. Examples include the DSM-5.1, DSM-5.2, and DSM-5.3 for incremental updates.
Note that the incremental updates will stop when a new edition of the DSM is available. The goal of the changes is for the APA websites to show when research supports a change in the manual. Due to consistent studies, the research base of different mental disorders is increasing.
Final Thoughts
DSM-5 is imperative because it offers a general language for mental health professionals and clinicians to understand and accept the terms of vital client information. It ensures there’s a consistent and dependable DSM 5 diagnosis for research on mental disorders, including addiction.
